Blog
Perspective
Explore our perspective on SEO, PPC, Data, Digital Consumer Intelligence and more.

How to Write SEO Engineering Tickets That Streamline Implementation
A Section-by-Section Framework With Tips, Tactics, and Examples
Read the blog >
How Do AI Bots Crawl the Web & What Does It Mean for Your Site?
A Guide to Auditing Crawl Accessibility & Quality From a GEO Perspective
Read the blog >
How to Optimize Pagination for SEO
A Guide to Getting Things Right While Serving a User-First Implementation
Read the blog >

If LLMs Are the Future of Search, What Should My Business Do Today?
Need-to-knows about LLM brand visibility & benchmarking for marketing leaders.
Read the blog >
Diagnosing Common JavaScript SEO Issues
How to Connect the Dots from Onsite Symptoms (Even If You’re Not a Dev!)
Read the blog >

Crawling & Indexing in SEO
How to Use Robots.txt, Meta Robots, and Canonical Tags Correctly
Read the blog >

DMI Insights
Turning Everyday Marketing Data Into Game-Changing Market Intelligence
Read the blog >

Implementing an SEO QA Process & Checklist
Turn Quality Assurance Into SEO Insurance
Read the blog >

Organic Traffic Down?
Don't Panic! Here's How To Find & Diagnose the Real Issue
Read the blog >

How to Write SEO Product Requirements Documentation
Serve Stakeholders & Streamline Projects
Read the blog >
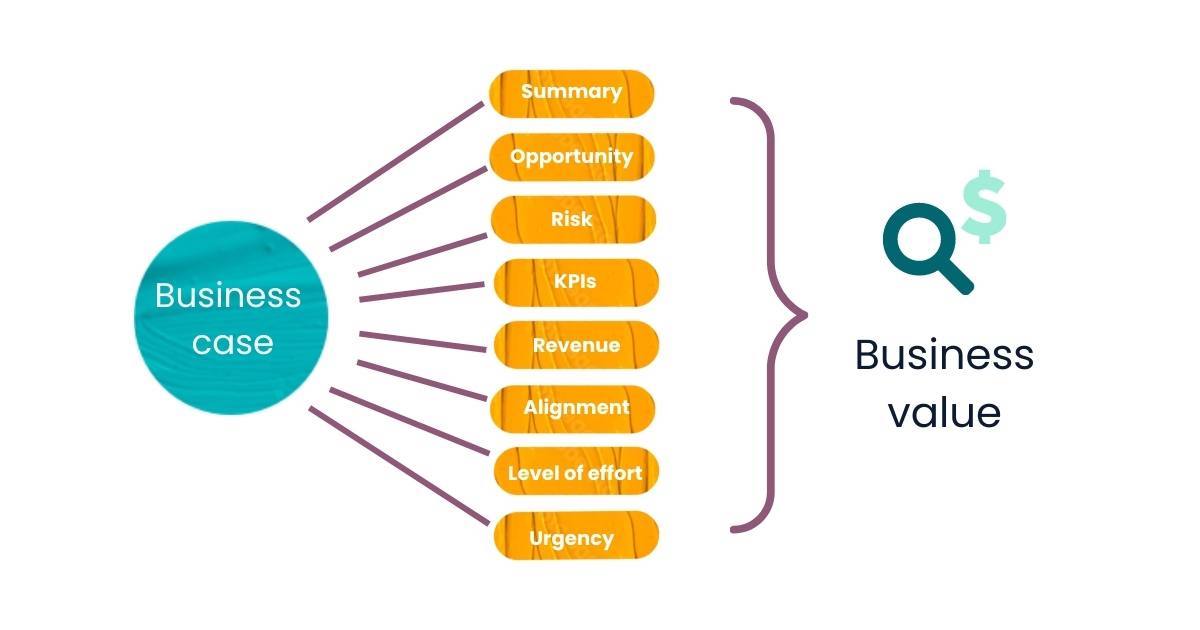
How to Create an SEO Business Case That Gets Traction
Read the blog >

9 Overlooked Examples of User-Generated Content That Drive SEO Growth
Read the blog >
How to Create a Marketing Measurement Plan That Defines What Matters
Read the blog >

The UGC SEO Playbook
How to Implement a Strategy That Sparks Scalable, Automated Growth
Read the blog >

Content Pruning SEO
How to Resolve Cannibalization & Improve Quality 🤝
Read the blog >
![Next-Gen SEO Content Planning & Keyword Matrix [Free Airtable Template]](https://assets.thegray.company/f/1016570/1250x712/e3e00e513f/airtable-content-seo-keyword-matrix-template-og-image.jpg)
Next-Gen SEO Content Planning & Keyword Matrix
A Free Airtable Template
Read the blog >

Scaling SEO: A Framework
Read the blog >

How to Plan & Implement Schema Markup, Avoiding Common Mistakes
Read the blog >

Brand Positioning & SEO
Aligning User Intent, Data with Brand Strategy
Read the blog >
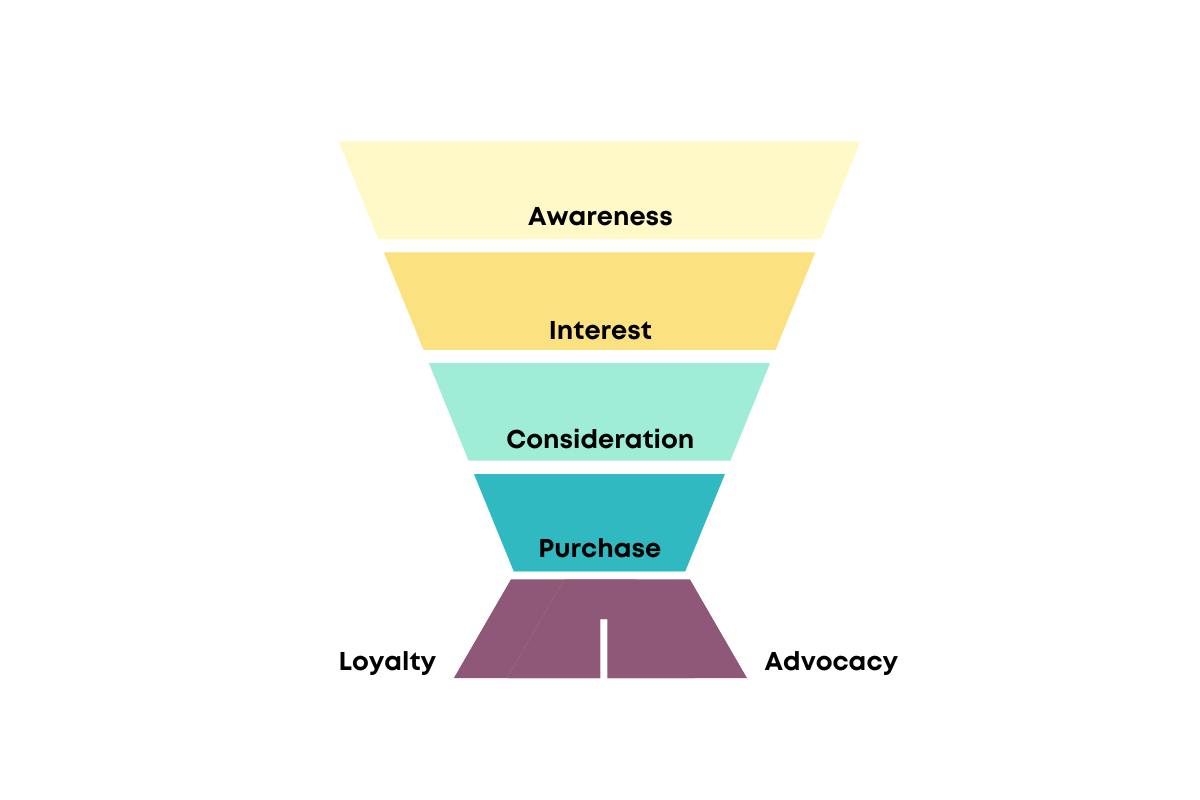
The SEO Customer Funnel
KPIs & SEO Metrics Worth Monitoring
Read the blog >

PPC Audit Methodology
An Expert's Workflow + Real-World Examples
Read the blog >

How to Work With Zero Search Volume Keywords
A Process for Finding & Leveraging Low to No-Volume SEO Keywords
Read the blog >

SEO for Startups Part II
What SEO Elements to Leverage and When?
Read the blog >

Should Your Startup Do SEO Now?
The “It Depends” Startup SEO Question List
Read the blog >

Information Architecture Best Practices for Advanced SEO & UX
Read the blog >

The eCommerce Technical SEO Framework
Making the Ambiguous Approachable
Read the blog >

How to Level Up Internal Linking for SEO, UX, & Conversion
Read the blog >

How to Do A JavaScript Audit for SEO
Read the blog >

Personalization & SEO
How to Optimize for Personalized Search
Read the blog >

Free SEO Templates from the SEO Community
Kickoff & Improve SEO Work
Read the blog >

How to Handle Permanently and Temporarily Out-of-Stock Products for eCommerce SEO & UX
Read the blog >
Duplicate Content & International SEO, Hreflang
Read the blog >

UX and SEO
How UX Design Can Help With SEO Concerns
Read the blog >

Best Practices for Faceted Navigation & SEO
eCommerce Facets, Filters, and Sort Order
Read the blog >
How to Create an SEO Roadmap
Connecting the Dots Between Strategy & Success
Read the blog >

What's in an SEO-friendly URL?
Best Practices for URLs
Read the blog >

How to Recover Traffic If a Migration Goes Wrong
Read the blog >

How to Plan an SEO Migration Strategy for Your Website
Read the blog >

The Art of Keyword Selection
How to Find, Choose, & Use the Best Keywords for SEO (and Conversions)
Read the blog >

How To Properly Serve Up 404s on Single Page Application (SPA) Pages for SEO
Read the blog >

SEO Internationalization Best Practices & QA Checklist
Read the blog >

Should I Choose a Multiple Domain SEO Strategy?
The Why, What, When
Read the blog >

International SEO Technical Specs (+ Business Decision Insights)
Read the blog >

Error 404 Guide for SEO & Usability (FAQs & More)
Read the blog >

How to Deindex "Stuff" from Google Quickly & Effectively
Read the blog >

Google Search Console Errors
A Guide to Finding & Fixing the Most Common GSC Errors
Read the blog >

50+ of the Best SEO Resources
Tools, Educational Resources, and More
Read the blog >